In building automation each time more coexist multiple automation protocols that must be integrated in a single system with the idea to have a unique Building Management System (BMS). The need to monitor different information and store it in a data base for a further analysis is even more requested any time. Energy saving in buildings is already a reality and not only a desire, and the way to have an energy efficient building is to measure different parameters like temperature, humidity, active power, reactive, etc. to determine where the energy is wasted on the building and where to take decisions in order to reduce the consumption of the building.
In all this measuring process, multiple electronic devices should be needed and managed on the building. For this reason the main topic to have in mind is to know which parameters must be measured and what devices will be used for.
When this exercise has been done, we will see that probably some products from different manufacturers will be needed and for this reason we should think on how to integrate them in a single monitoring station and unique data base.
Building automation installations are mainly based on standard protocols like LonWorks and BACnet, using the existing 100Base-T Ethernet channel to transmit information to the main central station where an SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition) application is used for data monitoring. But different monitoring points are mainly done using different control devices like energy meters, network analyzers that measure active power, reactive, harmonics, etc., temperature sensors, humidity, etc. Not all the monitoring devices are using the same communication protocol and for this reason we will need a device to monitor the different channels to convert them in a single protocol and send it over the right channel. For example, energy monitoring is mainly done by a network analyzer and we will find this device on the market with a Modbus RTU protocol and an RS-485 channel to share data with other devices. On the other hand, parameters like temperature, humidity, pressure, etc. will be found on the market in LonWorks, BACnet or KNX mainly.
The way to convert all those protocols in a single protocol for main supervision, is using a multiprotocol gateway like @LINX-100@http://www.e-controls.es/lighting/servidores-automatizacion/linX-100-lon...@ for LonWorks, @LINX-200@http://www.e-controls.es/lighting/servidores-automatizacion/linX-200-bac...@ for BACnet or @LGATE-900@http://www.e-controls.es/lighting/pasarelas-multiprotocolo/lgate-900/195...@ or LGATE-950 for LonWorks, BACnet and Modbus TCP in Ethernet.
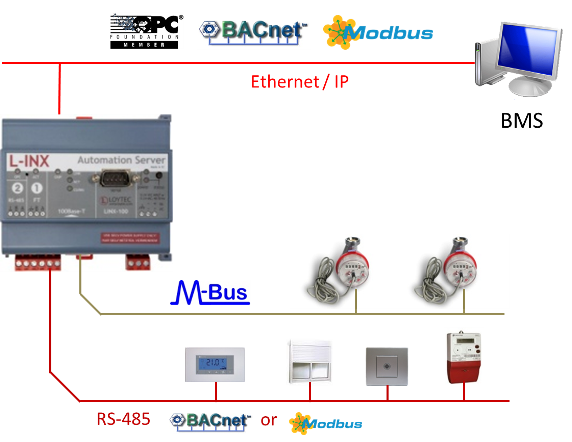
The LINX-200 gateway is including different field buses like BACnet, following the ISO 16484 standard, using the Rs-485 twisted pair channel for the automation part, where we will usually have temperature sensors, humidity, etc. for building monitoring and control. The device is also sharing the RS-485 channel for Modbus RTU that can be used for network analysis monitoring to check different the electrical parameters of the building. Finally, an RS-232 channel talking M-BUS can be used for water and gas meter monitoring. For this case we will add an external level converter to translate RS-232 voltage levels to M-BUS, different models according to the number of meters defined on the channel. All this monitoring information will be found on the LINX-200 device as datapoints or monitoring points and will be sent over the Ethernet channel up to a BMS station. But on the Ethernet channel there coexist also different protocols where we can find BACnet over IP (also known as BACnet/IP), Modbus TCP and an OPC Server XML-DA, that helps the integrator use the gateway for any kind of installation where protocol flexibility is required.
The LINX-200 gateway is the particularly indicated device to integrate multiple communication protocols in a BACnet based building, with the aim to send the information through a single communication channel to a building management BMS station.










 | Passatge Garrotxa, 6 | 08830 Sant Boi de Llobregat | Barcelona | Spain | Tel.: +34 93 652 55 21 | Fax +34 93 652 55 22
| Passatge Garrotxa, 6 | 08830 Sant Boi de Llobregat | Barcelona | Spain | Tel.: +34 93 652 55 21 | Fax +34 93 652 55 22